×
- Live Chat
- 1-888-958-2959

My Garage
My Account
Cart
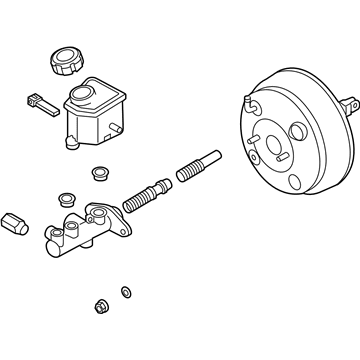
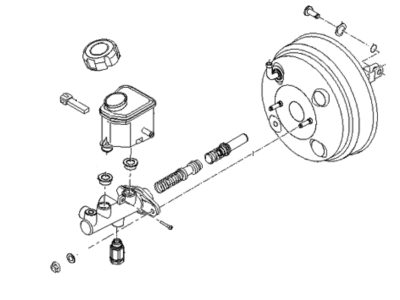
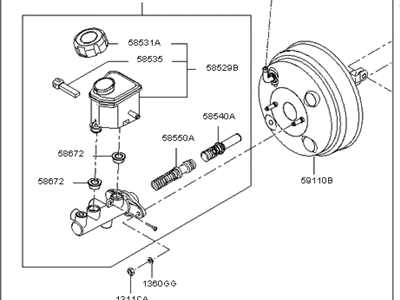
Genuine Kia Optima Brake Booster
Brake Power Booster- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
20 Brake Boosters found
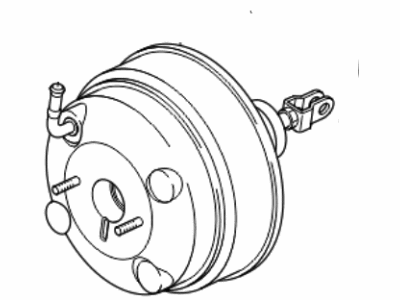
Kia Optima Booster Assembly-Vacuum
Part Number: 591103Q500$437.20 MSRP: $629.25You Save: $192.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Vacuum
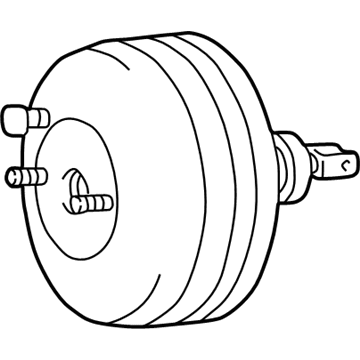
Part Number: 591102T200$298.88 MSRP: $430.17You Save: $131.29 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 5911038306$487.15 MSRP: $715.35You Save: $228.20 (32%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
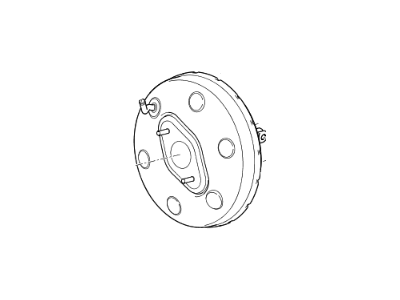
Part Number: 591102G200$263.91 MSRP: $379.84You Save: $115.93 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G210$335.40 MSRP: $471.74You Save: $136.34 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G100$342.52 MSRP: $492.99You Save: $150.47 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G110$342.52 MSRP: $492.99You Save: $150.47 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G200$350.51 MSRP: $492.99You Save: $142.48 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G400$376.50 MSRP: $529.54You Save: $153.04 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master
Part Number: 585002G410$380.22 MSRP: $534.77You Save: $154.55 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G300$382.06 MSRP: $549.89You Save: $167.83 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster & Master Cylinder
Part Number: 585002G310$382.06 MSRP: $549.89You Save: $167.83 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 591103C100$401.95 MSRP: $578.52You Save: $176.57 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 5911038007$456.62 MSRP: $670.52You Save: $213.90 (32%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 5911038006$457.92 MSRP: $672.42You Save: $214.50 (32%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 59110C1300$455.85 MSRP: $656.09You Save: $200.24 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 591102G100$263.91 MSRP: $379.84You Save: $115.93 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 59110C1050$412.94 MSRP: $594.33You Save: $181.39 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 59110C1400$421.58 MSRP: $606.77You Save: $185.19 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Optima Booster Assembly-Brake
Part Number: 59110C1450$421.58 MSRP: $606.77You Save: $185.19 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Optima Brake Booster
If you're in search of top-notch, reasonably priced OEM Kia Optima Brake Booster, then you've found the perfect spot. Our website boasts an extensive inventory of Kia Optima Brake Booster, all priced at the market's premier price. Rest assured, every genuine part we offer comes with a warranty straight from the manufacturer.
Kia Optima Brake Booster Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How do you inspect and service the brake system and brake booster on Kia Optima?A: For detailed photographs of the brake system, inspect the brakes every time the wheels are removed or whenever a defect is suspected. Symptoms indicating a potential brake system defect include the vehicle pulling to one side when the brake pedal is depressed, squealing or dragging noises when applied, excessive brake pedal travel, pulsating pedal, or brake fluid leaks, typically onto the inside of the tire or wheel. Begin by loosening the wheel lug nuts, raising the vehicle securely on jackstands, and removing the wheels. In disc brakes, each caliper contains two pads (outer and inner) that are visible with the wheels removed. Check the pad thickness by looking at each end of the caliper and through the inspection window; if the lining material is less than the specified thickness, replace the pads. If the thickness is difficult to determine, remove the caliper(s) and pads for further inspection, cleaning them with brake cleaner and re-measuring. Measure the disc thickness with a micrometer; if any disc is thinner than the specified minimum, replace it, and check for scoring, gouging, or burned spots, which may require resurfacing. Before reinstalling the wheels, check all brake lines and hoses for damage, wear, or leakage, ensuring they are clear of sharp edges and moving parts. For rear drum brakes, ensure the parking brake is off, remove screws around the drum, and tap the outside with a rubber mallet to loosen it. Clean the brake assembly with brake system cleaner, noting the lining thickness on the brake shoes; replace them if worn to within 1/16-inch of the rivets or if cracked or glazed. Ensure all springs are connected and check for fluid leakage from the wheel cylinder. Wipe the inside of the drum with a clean rag and check for cracks or imperfections that may require resurfacing. Repeat for the remaining wheel, and if all parts are in good condition, reinstall the brake drums and wheels. To check the brake booster, sit in the driver's seat and perform a series of tests: with the brake fully depressed, start the engine and observe if the pedal moves down slightly; with the engine running, depress the brake pedal several times to ensure the travel distance remains unchanged; then, with the engine off, hold the pedal for about 30 seconds to check for sinking or rising. Finally, check the parking brake by parking on a steep hill with the brake set; if it cannot prevent rolling, it requires attention.
Related Kia Optima Parts
Browse by Year
2020 Brake Booster 2019 Brake Booster 2018 Brake Booster 2017 Brake Booster 2016 Brake Booster 2015 Brake Booster 2014 Brake Booster 2013 Brake Booster 2012 Brake Booster 2011 Brake Booster 2010 Brake Booster 2009 Brake Booster 2008 Brake Booster 2007 Brake Booster 2006 Brake Booster 2005 Brake Booster 2004 Brake Booster 2003 Brake Booster 2002 Brake Booster 2001 Brake Booster 2000 Brake Booster